Affiliated Foot Care Center
Call 860•349•8500 or 203•294•4977
The crystallization of uric acid, often related to relatively high levels in the blood, is the underlying cause of gout. This can occur for a number of reasons, including diet, genetic predisposition, or underexcretion of urate, the salts of uric acid.
Underexcretion of uric acid by the kidney is the primary cause of hyperuricemia in about 90% of cases, while overproduction is the cause in less than 10%. About 10% of people with hyperuricemia develop gout at some point in their lifetimes.
The risk, however, varies depending on the degree of hyperuricemia. When levels are between 415 and 530 μmol/l (7 and 8.9 mg/dl), the risk is 0.5% per year, while in those with a level greater than 535 μmol/l (9 mg/dL), the risk is 4.5% per year.
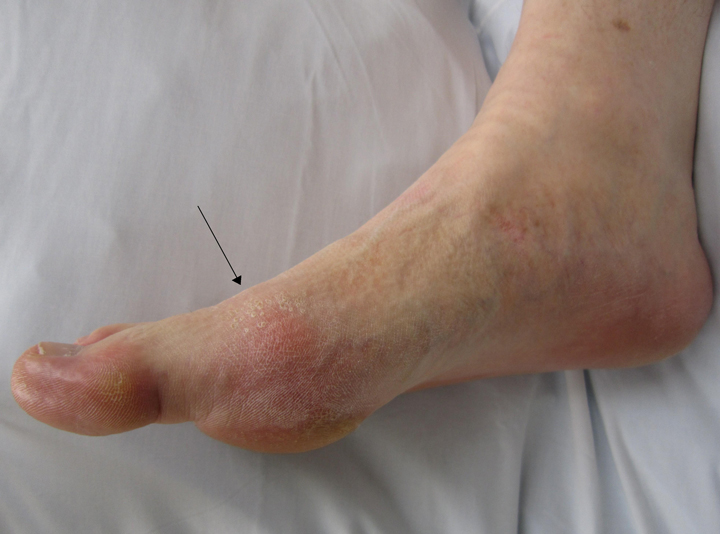
Gout is a disease hallmarked by elevated levels of uric acid in the bloodstream. In this condition, crystals of monosodium urate (MSU) or uric acid are deposited on the articular cartilage of joints, tendons and surrounding tissues. It is marked by transient painful attacks of acute arthritis initiated by crystallization of urates within and about the joints and eventually leads to chronic gouty arthritis and the deposition of masses of urates in joints and other sites, creating tophi. Gout results from a combination of prolonged elevation of uric acid and overall acidity in the bloodstream.
Gout is characterized by excruciating, sudden, unexpected, burning pain, as well as swelling, redness, warmth, and stiffness udually in your big toe. These attacks can happen over and over unless gout is treated. Over time, they can harm your joints, tendons, and other tissues. This occurs most commonly in men but women can also have a case of the gout as well.. You may also experience a low-grade fever. You usually suffer from two sources of pain: The uric acid crystals inside your joint will cause intense pain whenever you move it and the tissues around the joint will become inflamed and sore. The skin of the affected area will turn red and become very sensitive to touch, to the point of you not wanting to place a blanket over your foot at night.
We can prescribe pain relief medications as well as topical creams to reduce the sensitivity of your skin. We will also check you for any fungal infection, which may accompany the gout and treat it as well. If you don't treat gout quickly, surgery may be necessary to remove the large tophi and correct joint deformity.